












Business Economics
Inhouse product
-
Rs212.50
Rs250.00 -
Rs254.15
Rs299.00 -
Rs288.00
Rs300.00 -
Rs255.00
Rs300.00 -
Rs276.25
Rs325.00 -
Rs136.00
Rs160.00
Reviews & Ratings
Business Economics
Author: Anupam Sarma
A Textbook of Economics for B.Com & BBA
Published by Mahaveer Publications, Dibrugarh, this comprehensive textbook is designed for B.Com 3rd Semester (Dibrugarh University), BBA 4th Semester (Nagaland University), and other Indian universities.
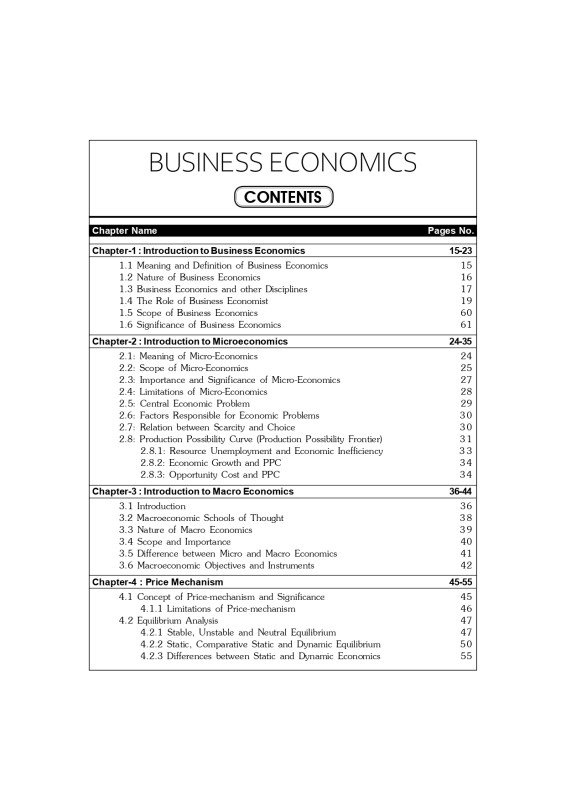
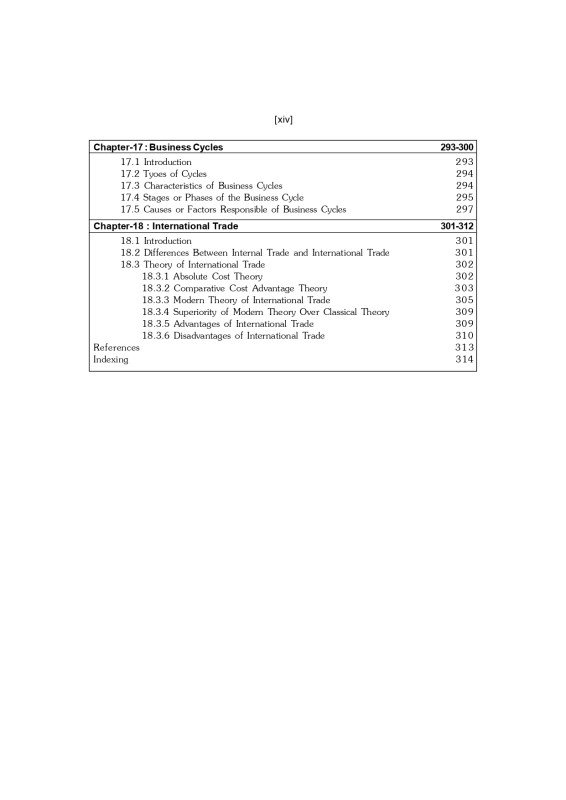
Table of Contents:
? Chapter 1: Introduction to Business Economics
? Chapter 2: Introduction to Microeconomics
? Chapter 3: Introduction to Macroeconomics
? Chapter 4: Price Mechanism
? Chapter 5: Demand Analysis
? Chapter 6: Supply Analysis
? Chapter 7: Consumer Behaviour
? Chapter 8: Theory of Production
? Chapter 9: The Nature of Cost and Cost Curves
? Chapter 10: Market Structure
? Chapter 11: Monopoly
? Chapter 12: Monopolistic Competition (Pages 213-223)
? Chapter 13: Oligopoly (Pages 224-238)
? Chapter 14: Theory of Factor Pricing
? Chapter 15: National Income Accounting
? Chapter 16: Inflation
? Chapter 17: Business Cycles
? Chapter 18: International Trade
? A must-have for students looking to grasp the fundamental and advanced concepts of Business Economics.
Frequently Bought Products
Digital Fluency
Product Queries (0)
Login Or Registerto submit your questions to seller
Other Questions
No none asked to seller yet
-
Rs212.50
Rs250.00 -
Rs254.15
Rs299.00 -
Rs288.00
Rs300.00 -
Rs255.00
Rs300.00 -
Rs276.25
Rs325.00 -
Rs136.00
Rs160.00








